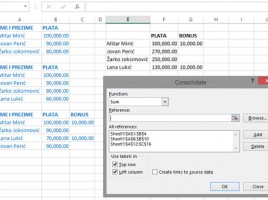
Creating Pivot tables
Pivot tables (Pivot table reports) are a tool for creating interactive reports based on the range of selected data or structured tables. Columns from source tables are used as reporting dimensions by aggregation of data (measures) or using them to analyze in rows, columns, as filters (dimensions) … Once made, the Pivot tables are easily changed by adding or removing dimensions, giving us more different look at the unique original dataset.