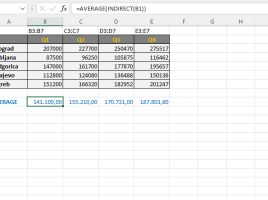
REDUCE function
The REDUCE function is used to reduce a given array to an accumulated value defined by the LAMBDA function. It is somewhat reminiscent of conditional data aggregation functions but provides far more possibilities. In the example that follows, you will be able to see its application for calculating the last day of the month when sales were higher than average.